|
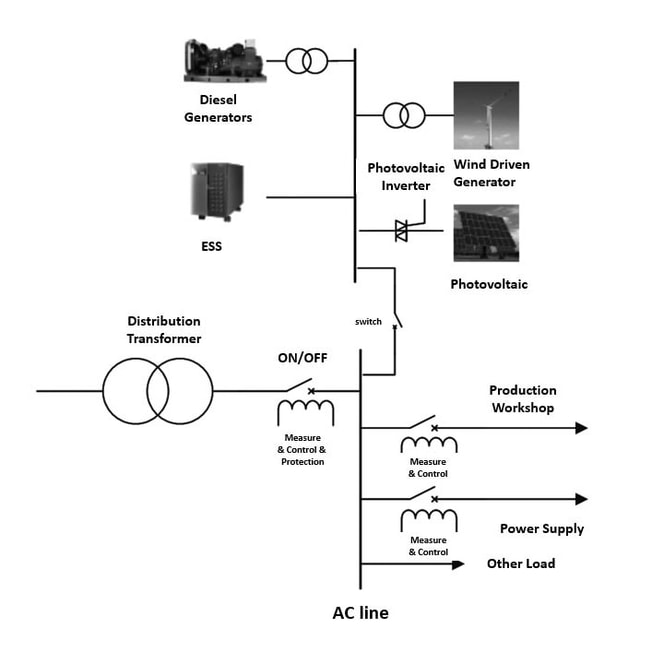
A Microgrid is an independent power system that can operate without being connected to the main grid. It usually consists of one or more generators, batteries and other energy storage devices that can meet the electricity needs of the local area. Microgrids are commonly used by local governments, schools, hospitals, rural and other remote areas, and to provide emergency power support in the event of a major power grid failure or disaster. Energy storage containers can be used as storage systems to help balance power supply and demand in microgrids and ensure the stability and reliability of power. The container energy storage system is connected to the busbar of the microgrid. Depending on the characteristics of the peaks and troughs, the microgrid charges the batteries in the troughs, stores the excess energy of the microgrid, and feeds the energy back to the grid during the peak. This helps reduce over-reliance on generators and improve the efficiency and economics of microgrids. Depending on the control of the microgrid system, wind and photovoltaic power generation systems can be connected to the bus; when connected to the busbar, energy such as wind power and photovoltaics can be stored, truly realizing "load regulation, matching new energy access, making up for line losses, and power compensation.”, improve power quality", and can also realize the function of isolated grid operation. The energy storage battery cluster is in standby state after charging and can be fed back to the grid under the uniform control of the background. Containerized energy storage systems play an important role in microgrids, and their compact and modular design, combined with their versatility and reliability, make them ideal solutions for microgrid applications. Written by Mandy Comments are closed.
|
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
- Home
-
Containerised solutions
- Intelligent pressurised container | MUD logging cabin
- Battery energy storage system (BESS) container
- Flexible grid tied battery storage system
- Laboratory container | workshop container | Equipment containers
- Temporary refuge shelter | Toxic gas refuge | Safe haven
- Offshore accommodation cabin | office container
- Reefer container | Refrigerated container
- Intelligent waste water treatment container
- Fresh water generator container
- Cargo Containers
- Product photos & videos
- News & Blogs
- Contact us
|
Featured products
Intelligent pressurised container Temporary refuge (TR) shelter, toxic gas refuge (TGR) Battery energy storage system (BESS) container Containerised waste water treatment plant Fresh water generator container Reefer container Laboratory container, Workshop container Accommodation container Offshore closed container |
All Rights Reserved 2020 © TLS Offshore Containers / TLS Energy
|