|
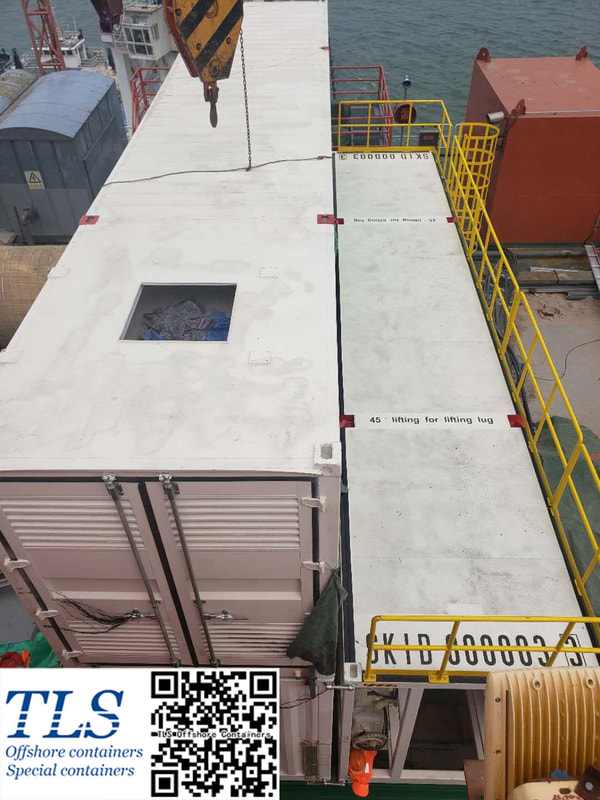
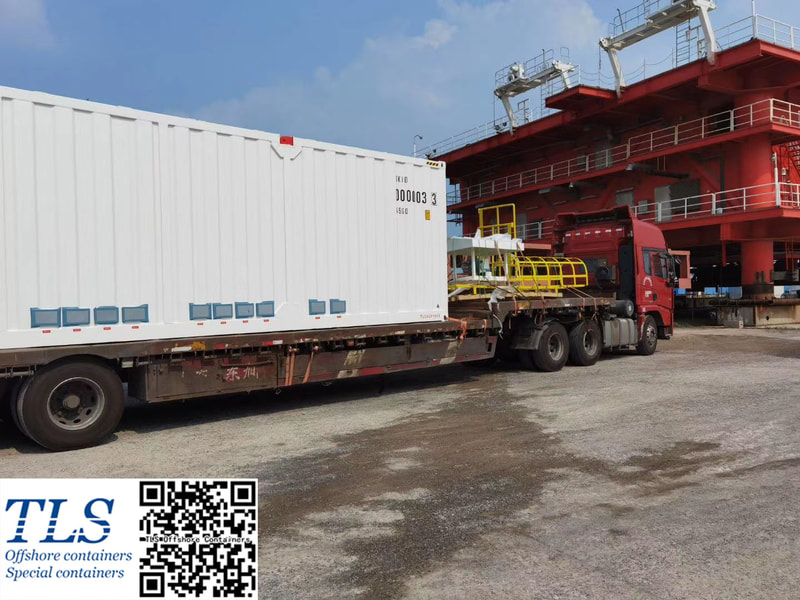
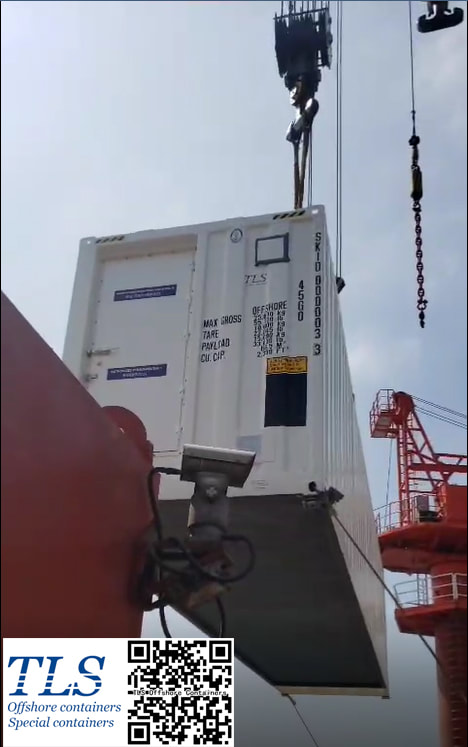
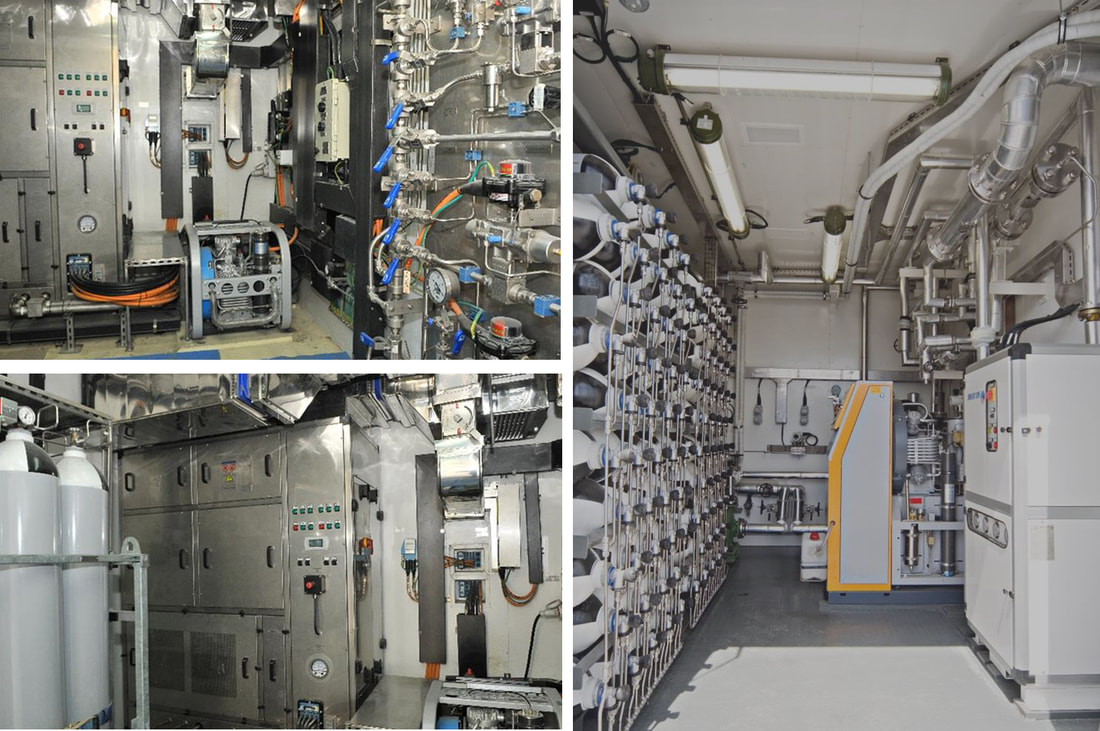
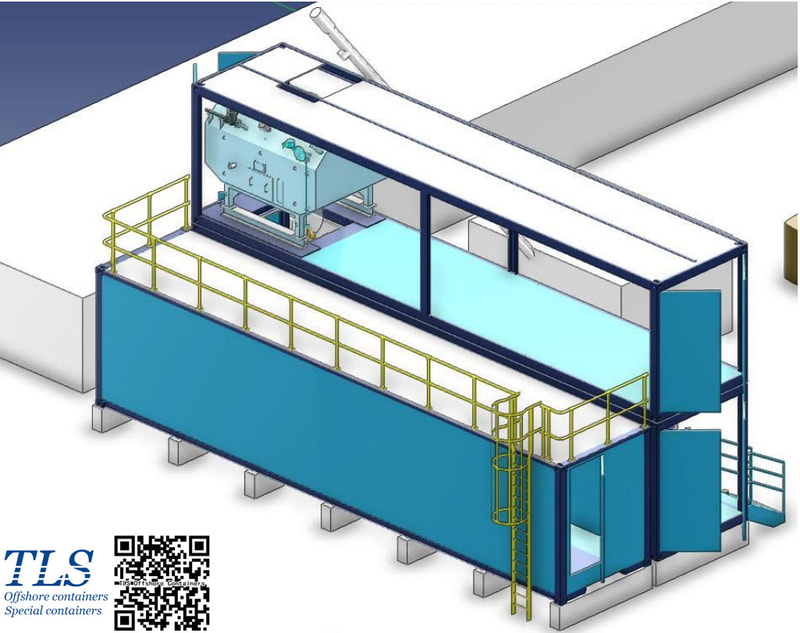
The tertiary recovery has become the dominant technique for the stable production of old oilfields in the Shengli Oilfield. The cumulatively incremental oil was up to 11.50 million tons by the end of Mar/2006. Chemical flooding has developed from single polymer flooding to multiple compo und flooding systems in the oilfield, and a complete set of chemical flooding with the oilfield's characteristics was formed. The tertiary recovery is facing some major problems, such as inadequate high-quality resources of the polymer flooding, replacement difficulty and unbalanced development of the tertiary recovery technology, and great resulted differences among the chemical-flooding implemented units , etc. The chemical flooding technology and the ability to innovate new products should be strengthened. The developmental space of tertiary recovery should be widened through continuously extending technical storage. The polymer-injection project should be well managed so as to enhance the effect of water decreasing and oil increasing. The intensive pilot study will make the tertiary recovery technology replacement faster. TLS is honored to work as a partner of the subcontractor involving the Shengli oilfield project. The pressurised MCC shelters manufactured by TLS are used in the oilfield. The purpose of a temporary refuge shelter (or safe haven, H2S refuge shelter, or shelter in place) is to keep you safe when a chemical release or blast cause severe health effects. Toxic gases produced from an explosion or loss of containment, when inhaled, can lead to disorientation, incapacitation or death. Two protective actions commonly used in the event of a blast or chemical release are evacuation or to seek temporary refuge in a shelter in place or safe haven. Time, size of the hazard, and location are just a few variables which can impact your ability to evacuate safely. When evacuation is not possible, the shelters will provide a safe alternative and are an essential part of emergency management. Installation protective shelters such as safe havens, blast-resistant buildings and SIPs, is a mitigation control to reduce the loss of life, and damage to property and equipment, when preventative controls fail, When it comes down to it, these shelters help to improve survivability.
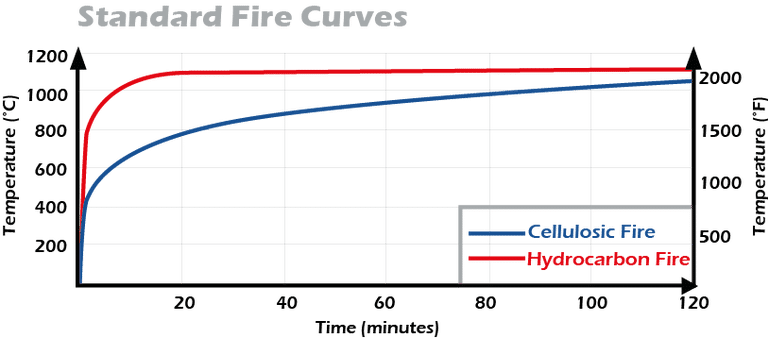
Fire ratings such as A60 and H120 indicate the duration the doors and walls must be able to withstand a particular type of fire. Difference between A- and H-fire ratings A-fire rated doors and walls are tested with a ISO cellulosic fire temperature curve. H-fire rated items are tested with a hydrocarbon fire curve. The hydrocarbon fire curve has a faster build-up and higher plateau temperature than the standard A-curve. The fire doors and fire walls shall maintain their function with respect to fire resistance and structural integrity when exposed to a heat load characteristic for cellulosic (A-fire rating) fire or hydrocarbon (H-fire rating) fire.
|
Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
- Home
-
Containerised solutions
- Intelligent pressurised container | MUD logging cabin
- Battery energy storage system (BESS) container
- Flexible grid tied battery storage system
- Laboratory container | workshop container | Equipment containers
- Temporary refuge shelter | Toxic gas refuge | Safe haven
- Offshore accommodation cabin | office container
- Reefer container | Refrigerated container
- Intelligent waste water treatment container
- Fresh water generator container
- Cargo Containers
- Product photos & videos
- News & Blogs
- Contact us
|
Featured products
Intelligent pressurised container Temporary refuge (TR) shelter, toxic gas refuge (TGR) Battery energy storage system (BESS) container Containerised waste water treatment plant Fresh water generator container Reefer container Laboratory container, Workshop container Accommodation container Offshore closed container |
All Rights Reserved 2020 © TLS Offshore Containers / TLS Energy
|